The article was updated on November 15, 2023.
Food and technology may not seem like an obvious pair, but in today’s world of a growing population and increasing demand, the food industry is experiencing a rapid technological transformation. These days, consumers expect healthier, safer, and cheaper products, implying that food production should become more efficient, cost-effective, and higher in quality. In response, new, promising food tech startups enter the market every year.
The technology impact on the food and beverage industry is hard to miss, and the future is already reshaping it. Recent data shows that the food technology market is expected to go over $360 billion in just five years. To compare, in 2022, this market was evaluated at $260.07 billion.
How can your company join? We are going to cover the emerging technologies in the food industry and how you will benefit from them. By starting with at least one of these points, you will begin to notice the difference.
How market drives the changes in food and beverage
The world around us is changing, and so does our attitude to what we eat. Evolving digital opportunities along with an eco-responsible approach are inducing changes in food production. These are the four main factors that are causing the food industry revolution.
1. Demand for safe and healthy food
Food production is growing fast, but it does not always mean that it is safe for customers. High quality is the key factor that should be considered by manufacturers, and that is why more and more regulations have appeared in the F&B sector.
Take the recent EU food regulations coupled with the growing demand for healthy and “clean” products and thus, new challenges have surfaced for food and beverage manufacturers. How can you achieve the highest level of quality and not damage the brand’s image? The latest tech trends seem to provide the best solutions.
A recent ING report proves that consumers expect to see healthier food on the store shelves in the future. 43% of respondents are looking for healthy options, while 18% are interested in eco-friendly products:
2. Climate change
The planet’s wellbeing is now disturbing the minds of thousands of people, and all of them need food for everyday living. We see how numerous consumers are choosing a plant-based diet and expect more sustainability from manufacturers. Creating transparency and proving sustainability in the production process is viable only with a digital transformation in the food industry.
3. Reducing of plastics waste
Using plastic-free straws, cups, and plates is a growing worldwide trend. Some countries moved even further and banned plastic cutlery altogether. What is next?
Food and beverage companies should adapt their packaging to this trend and come up with alternative solutions for packaging systems. When the old methods do not work, the digital world swoops in to help.
4. Fierce competition
The F&B industry includes huge numbers of manufacturers and retailers, and each of them is fighting for a place in the sun.
Moreover, the most popular F&B companies create their own markets with innovative products that meet the latest demands of their target audience. Appearing on the store shelf looks like a savage race for every participant. But at the same time, creating an innovative product means more time, costs, and employees – the solution to all that is in the digital tools.

What is food tech?
So, how is technology changing the food industry? In short, food tech is the integration of technological innovation and science into various aspects of the food and beverage industry. It focuses on improving food production, processing, safety, and consumption. From enhancing agricultural practices to online food delivery and dietary apps, food tech solutions address efficiency, sustainability, and consumer health.
Overall, the food tech industry pursues such goals as
- producing sustainable food and beverage packaging materials and smart packaging to minimize food waste,
- streamlining food ordering and distribution by investing in online food delivery platforms,
- empowering consumers to make informed nutritional choices via dietary apps and other tools,
- enhancing agricultural practices and crop management with various food tech innovations,
- creating a more convenient and efficient cooking experience with cooking gadgets and smart kitchen technology,
- developing alternative ingredients and innovative diets such as plant-based and lab-grown meat products, to meet specific dietary needs and sustainability goals,
- extending the shelf life of products, improving food safety, enhancing the nutritional value of processed foods, and more.
What are the key benefits of digital transformation in food and beverage manufacturing?
Investing in modern software and digital tools requires some consideration from business owners. But with time, more and more companies opt for the digital transformation. Why would they do that? Here is a list of benefits that answer this question.
1. A more accurate supply and demand forecast
Inventory is a big part of food processing operations requiring a sizable investment in both buying and storing necessary products. When companies know the demand beforehand, it keeps the cash flow in order and reduces risks.
Software with advanced analytics affords us the ability to better understand customer needs and predict more accurately the seasonal levels of demand.
2. Reduced risks of the equipment breakage
Using smart sensors is a revelation for many industries, including the food and beverage. Such devices are used to identify any equipment anomalies at an early stage, which allows companies to extend the life cycle of some machines and avoid downtimes.
Also, some supply chains deal with products and ingredients that should always be fresh. In this case, controlling the temperature and humidity is vital for the production process, and smart sensors are the best at identifying any deviations.
Read also: The Future of the Digital Workforce in Manufacturing
3. Improved customer experience
The faster the time flies, the more choices your customers get: the market is overloaded with products and services. That is why many brands are working hard to transform products into something bigger – products become services, and services are turned into experiences.
Food industry technology innovations allow business owners to understand customers better and provide them with a little bit more than they expect. For example, the latest quality management and traceability software prevents any low-quality products from appearing in the consumer’s hands. It both increases your income and improves your market reputation.
Already a quarter of Dutch consumers want to know more about the origins of the meat they buy, fruit and vegetables are next on the list:

4. Recipe flexibility in changing conditions
While consumer demands are changing, food manufacturers should always be ready to adapt. They have to change the products’ packaging, recipes, and deliver new products faster to the market.
Digital recipe management tools make brands flexible in this regard, allowing them to save more by spending less on possible changes: operations with several streams and products are now managed more efficiently.
5. Safer production environment
The food industry’s digital transformation concerns not only customers but also workers who produce products for them. Workers complete their tasks more effectively in a safe environment, and digital tools provide all of that.
AR software along with training simulators help notice and calculate the machinery’s working parameters and provide necessary real-time data right in front of the engineer.
Read also: 7 Ways Augmented Reality Transforms Manufacturing
6. Increased efficiency and productivity in food production
The adoption of digital transformation within the food industry also means increased automation and data-driven decision-making of work processes at all stages, from farming and manufacturing to delivery. Not only do such processes reduce the need for manual labor, which also reduces human error, but also promise waste reduction in food production.
Food and beverage companies can fully rely on technology to refine production planning, and resource allocation, leading to higher efficiency and productivity.
7. Improved food safety and quality control
Modern technology used in the food industry ensures that the production environments meet the highest safety standards.
For example, the integration of blockchain technology introduces an additional layer of security, offering real-time monitoring and advanced quality control systems. It allows for the tracking of product origins and journeys, thus simplifying the identification and safety control.
8. Greater focus on sustainability and health
Food industry technology innovations are instrumental in achieving global sustainability goals. These innovations facilitate the optimization of resource usage, reduced energy consumption, and a decrease in waste within the F&B industry.
They also empower manufacturers to create healthier products by closely monitoring nutritional content and consumer preferences, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable and health-conscious food options.
9. Increased transparency and traceability
IoT technology can improve transparency and traceability within the food industry by using sensors for real-life monitoring. These sensors can track temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions during transportation, ensuring food safety and quality.
Such a novelty allows for a true digital transformation in the food industry, as it ensures product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance while reducing waste, minimizing fraud, and empowering consumers with detailed product information.
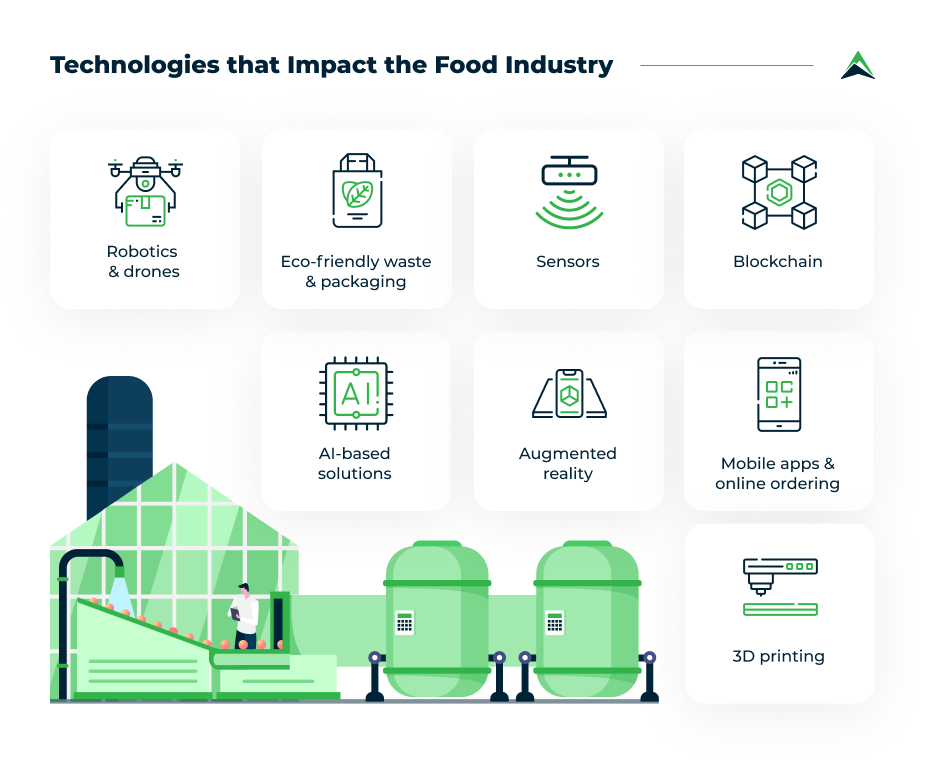
Technologies that impact the food industry
And here is the most interesting part – what are the exact innovations that are now transforming the F&B industry? We have gathered the most interesting examples.
Robotics
Various tech devices are aimed at making food production faster and safer. Only advanced machines can keep products and their ingredients in perfect conditions. But this is not the only example.
Read also: How to Optimize Supply Chain through IoT, Analytics and Automation
Robots can also assist people in coping with their everyday tasks. Back in 2016, the largest meat processing company in the world, JBS, first tried out “robot butchers” that could cut the most difficult sections of the meat. Butchers cutting these more challenging pieces of meat certainly makes their job more dangerous, but robots have created a safer environment and reduced the risk of injuries.

Drones
The agriculture industry is setting up lots of challenges for business owners – the sphere is strongly dependent on weather conditions and the quality of soil and crops. Without the use of technology, workers have to physically check every patch to make sure the outcome will be positive.
To provide a product of the highest quality, some companies have started using drones. How does it help? Drones get a general overview of the field from above and then test both the soil and crops. These small helpers deliver information to the farmworkers and help them identify which crops are damaged. As a result, it saves lots of time, helps grow only high-quality crops, and improves workers’ productivity.
Read also: Why Use Agriculture Drones? Main Benefits and Best Practices
Eco-friendly waste and packaging
As consumers now are strongly focused on sustainability and healthy meals, brands have no other choice except to follow up with this trend.
What alternatives do we have? With the latest tech developments, there are actual edible packaging with zero waste and micro packaging which involves using nanoparticles that even kill bacteria.
Technologies can also help fight against product waste. The Copia app connects shops and restaurants that have a surplus in available food with numerous nonprofit organizations that are happy to accept it.
Sensors
Smart sensors transform the physical world of the production process into digital data and provide managers with priceless insights. Sensors can count inventory and food ingredients making the manager’s work more efficient.
Also, these smart devices get real-time data about the production’s assets and distinguish critical items that can potentially cause downtimes.
Sensors control the steps of every product and check food and beverage conditions while the products are on the way to the buyer. The biggest problem in this case is maintaining stable temperatures. Smart sensors can be deployed in vehicles, refrigerators, displays, etc. to avoid deviations. If any issue occurs, workers get information via a mobile or desktop app.
Blockchain
In the modern age, transparency rules. We want to know more about the world around us and share our personal and professional lives with others. It is the same when it comes to food: we are trying to find a detailed list of ingredients and make sure the production process is safe enough for the environment.
For instance, Provenance went the innovative way and used blockchain to provide information about the product’s origins. Potential buyers only scan the ID mark on the product with their smartphones and can see the chain of custody from the very beginning.
AI-based solutions
How many products should you produce in a day, week, or month? Without these numbers, a production process is nothing more than a blind walk in the dark. AI-powered solutions provide an accurate forecast for companies of any size, using big data and updating it real-time.
But food production is not the only branch requiring an accurate forecast – let’s not forget about cafes and restaurants. The two crucial factors for any restaurant are the level of staffing and a well-stocked kitchen. Choosing wisely is not your everyday task anymore – AI-powered technologies do all the dirty work.
Complex restaurant management platforms can forecast staff demands, track every product and then order it according to the sales trends. There is no need to guess when you have real-time data in your hands.
Another food industry digital innovation is self-checkout kiosks – Aramark installed them at Major League Baseball stadiums. The main advantage of this novelty is that customers can check out several products at once without scanning barcodes – the computer vision works instead. It is a time-saver at crowded places and allows for the fastest check-out process.
Read also: Driving Digital Transformation through AI
Augmented Reality (AR)
Used in both the restaurant and food retail sectors, augmented reality is among the major emerging digital trends in the food and beverage industry. Restaurants have adopted AR to enhance the dining experience. Customers can use AR apps to view interactive menus, which might display detailed information, images, and even videos of menu items. This allows for a more immersive and informative dining experience.
In food retail, AR is used for product visualization. For instance, shoppers can scan product labels via phone cameras and receive additional information about ingredients, nutritional value, and even recipe suggestions.
Mobile apps and online ordering for food and beverages
Mobile apps and online ordering platforms have revolutionized how consumers access and order food. Food delivery apps enable users to browse menus, place orders, and track deliveries with ease. These apps often feature customer reviews, ratings, and recommendations, providing a convenient way to discover new eateries.
Additionally, mobile apps can support loyalty programs and personalized offers, improving customer engagement and retention for both restaurants and food delivery services.
3D printing
3D printing is an emerging technology in the food industry with the potential to transform food production. It enables the creation of intricate food designs and customized shapes that are challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
This technology is being explored in areas like pastry and confectionery, where chefs and bakers can craft unique and artistic food items. 3D printing also has the potential to personalize food by customizing ingredients and nutritional content to meet specific dietary requirements.
Examples of how various food sectors use technology
Let’s explore the examples of how emerging technologies in the food industry reshape various food sectors, from agriculture and food science to food consumer services, aiming to improve efficiency, quality, and the overall consumer experience.
Agriculture tech
- Precision agriculture: Farmers use GPS technology, sensors, and data analytics to optimize planting, irrigation, and harvesting. For instance, tractors equipped with GPS can precisely plant seeds and apply fertilizers, reducing waste and increasing crop yields.
- Drones: Drones are used for aerial crop monitoring. They can capture images and data to assess plant health, detect diseases, and identify areas that need attention.
- IoT sensors: IoT sensors are used to monitor soil conditions, weather data, and the well-being of livestock. For instance, sensors can provide real-time updates on soil moisture, helping farmers make better decisions about irrigation.
Food science
- Nanotechnology: Food and beverage manufacturers use nanotechnology to enhance food quality and safety. For example, this technology can improve the stability of sensitive food components, such as vitamins or flavors.
- Sensory analysis: Technology assists in sensory analysis, where instruments can measure and analyze taste, texture, and aroma to fine-tune food products and create a consistent consumer experience.
- Gene editing: In biotechnology, we can enhance crops and livestock resistance to diseases, improve nutritional profiles, and increase yields by using gene editing techniques. This technology opens the possibility of improving food security and sustainability.
Food service
- Point of Sale (POS) systems: Restaurants and cafes use POS systems for order processing, payment, and inventory management. The technology used in the food service industry streamlines operations and enables data analysis for better decision-making.
- Tablet menus: Some restaurants employ tablet-based menus that allow diners to browse, customize orders, and make payments electronically, enhancing the dining experience.
- AI-Powered chatbots: Some restaurants and fast-food chains employ AI-powered chatbots for customer service. Customers can place orders, inquire about menu items, and receive assistance through chatbot interfaces, improving customer service efficiency.
Delivery
- Food delivery apps: Companies like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and others connect consumers with restaurants for convenient online ordering and delivery. GPS tracking in these apps lets customers monitor the delivery process in real time.
- Delivery robots and drones: Currently, delivery robots and drones are being tested for autonomous food delivery. These technologies aim to reduce delivery times and costs.
- AI-Optimized routing: Delivery companies utilize AI algorithms for route optimization. These algorithms consider traffic, delivery windows, and order locations to create the most efficient delivery routes, reducing delivery times and fuel consumption.
Consumer services
- Personalized nutrition apps: Apps and online platforms use data from wearable devices and user input to provide personalized dietary recommendations. They track and analyze users’ nutrition, physical activity, and health goals.
- Smart appliances: Smart kitchen appliances, like refrigerators with built-in cameras and connected ovens, provide consumers with real-time monitoring and control of their kitchen, from tracking food inventory to adjusting cooking settings remotely.
The world changes, and so does the food
The green movement, climate change, the growth of competition – all these factors make F&B companies look for new ways to improve their products and services. Old-school methods will not work because they cannot provide the highest levels of transparency, quality of product shipment, and storage. Instead, marketers choose the latest tech innovations.
Now brands use technologies such as robots, drones, sensors, and artificial intelligence – the impact that they have on the food and beverage industry should not be underestimated. It is not only about food ingredients – it is about plastic-free packaging, sustainability, improved storage conditions, and demand forecast.
Be it an IoT or AI-powered solution, Eastern Peak makes any transformation possible. Contact our development team and share your bravest ideas.
Read also:



