The article was updated on March 1, 2023.
With the growing adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), connected devices have penetrated every aspect of our life, from health and fitness, home automation, automotive, and logistics, to smart cities and industrial IoT.
Thus, it is only logical that IoT, connected devices, and automation would find their application in agriculture, and as such, tremendously improve nearly every facet of it. How could one still rely on horses and plows when self-driving cars and virtual reality are no longer a sci-fi fantasy but an everyday occurrence?
Farming has seen a number of technological transformations in the last decades, becoming more industrialized and technology-driven. By using various smart agriculture gadgets, farmers have gained better control over the process of raising livestock and growing crops, making it more predictable and improving its efficiency.
This, along with the growing consumer demand for agricultural products, has contributed to the increased proliferation of smart farming technologies worldwide. In 2022, the market share for IoT in agriculture reached $13.76 billion.
In this article, we will explore the IoT use cases in agriculture and examine their benefits. So, if you are considering investing into smart farming, or are planning to build an IoT solution for agriculture, dive right in.
What is smart agriculture? The definition and market size
There are many ways to refer to modern agriculture. For example, AgriTech refers to the application of technology in agriculture in general.
Smart agriculture, on the other hand, is mostly used to denote the application of IoT solutions in agriculture. What does smart agriculture using IoT entail? By using IoT sensors to collect environmental and machine metrics, farmers can make informed decisions and improve just about every aspect of their work – from livestock to crop farming.
For example, by using smart agriculture sensors to monitor the state of crops, farmers can define exactly how many pesticides and fertilizers they have to use to reach optimal efficiency. The same applies to the smart farming definition.

Although smart agriculture IoT, as well as industrial IoT in general, isn’t as popular as consumer connected devices, the market is still very dynamic. The adoption of IoT solutions for agriculture is constantly growing.
Namely, COVID-19 has positively influenced the market share of IoT in agriculture. Disruptions in the supply chain and the shortage of qualified workers have propelled its CAGR to 9.9%. In fact, as per recent reports, the smart framing market share is set to reach $28.56 billion by 2030.
At the same time, the global smart agriculture market size is expected to triple by 2025, reaching $15.3 billion (compared to being slightly over $5 billion back in 2016).
Because the market is still developing, there is still ample opportunity for businesses willing to join in. Building IoT products for agriculture within the coming years can set you apart as an early adopter and, as such, help you pave the way to success.
But why should you consider building an IoT application for agriculture in the first place?
The Benefits of smart farming: How’s IoT shaping agriculture
Technologies and IoT have the potential to transform agriculture in many aspects. Namely, there are 6 ways IoT can improve agriculture:
- Data, tons of data, collected by smart agriculture sensors, e.g., weather conditions, soil quality, crop growth progress, or cattle health. This data can be used to track the state of your business in general as well as staff performance, equipment efficiency, etc.
- Better control over the internal processes and, as a result, lower production risks. The ability to foresee the output of your production allows you to plan for better product distribution. If you know exactly how many crops you are going to harvest, you can make sure your product won’t lie around unsold.
- Cost management and waste reduction thanks to the increased control over the production. Being able to see any anomalies in the crop growth or livestock health, you will be able to mitigate the risks of losing your yield.
- Increased business efficiency through process automation. By using smart devices, you can automate multiple processes across your production cycle, e.g., irrigation, fertilizing, or pest control.
- Enhanced product quality and volumes. Achieve better control over the production process and maintain higher standards of crop quality and growth capacity through automation.
- Reduced environmental footprint. Automation also carries environmental benefits. Smart farming technologies can cut down on the use of pesticides and fertilizer by offering more precise coverage and, thus, reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
As a result, all of these factors can eventually lead to higher revenue.

Now that we have outlined how IoT can be advantageously applied in the sphere of agriculture, let’s take a look at how the listed benefits can find their application in real life.
IoT use cases in agriculture (with examples)
There are many types of IoT sensors for agriculture as well as IoT applications in agriculture in general:
1. Monitoring of climate conditions
Probably the most popular smart agriculture gadgets are weather stations, combining various smart farming sensors. Located across the field, they collect various data from the environment and send it to the cloud. The provided measurements can be used to map the climate conditions, choose the appropriate crops, and take the required measures to improve their capacity (i.e., precision farming).
Some examples of such agriculture IoT devices are allMETEO, Smart Elements, and Pycno.

2. Greenhouse automation
Typically, farmers use manual intervention to control the greenhouse environment. The use of IoT sensors enables them to get accurate real-time information on greenhouse conditions such as lighting, temperature, soil condition, and humidity.
In addition to sourcing environmental data, weather stations can automatically adjust the conditions to match the given parameters. Specifically, greenhouse automation systems use a similar principle.
For instance, Farmapp and Growlink are also IoT agriculture products offering such capabilities, among others.
3. Crop management
One more type of IoT product in agriculture and another element of precision farming are crop management devices. Just like weather stations, they should be placed in the field to collect data specific to crop farming, from temperature and precipitation to leaf water potential and overall crop health.
Thus, you can monitor your crop growth and any anomalies to effectively prevent any diseases or infestations that can harm your yield. Arable and Semios can serve as good representations of how this use case can be applied in real life.

4. Cattle monitoring and management
Just like crop monitoring, there are IoT agriculture sensors that can be attached to the animals on a farm to monitor their health and log performance. Livestock tracking and monitoring help collect data on stock health, well-being, and physical location.
For example, such sensors can identify sick animals so that farmers can separate them from the herd and avoid contamination. Using drones for real-time cattle tracking also helps farmers reduce staffing expenses. This works similarly to IoT devices for pet care.
For example, SCR by Allflex and Cowlar use smart agriculture sensors (collar tags) to deliver temperature, health, activity, and nutrition insights on each individual cow as well as collective information about the herd.

5. Precision farming
Also known as precision agriculture, precision farming is all about efficiency and making accurate, data-driven decisions. It’s also one of the most widespread and effective applications of IoT in agriculture.
By using IoT sensors, farmers can collect a vast array of metrics on every facet of the field microclimate and ecosystem: lighting, temperature, soil condition, humidity, CO2 levels, and pest infections. This data enables farmers to estimate optimal amounts of water, fertilizers, and pesticides that their crops need, reduce expenses, and raise better and healthier crops.
For example, CropX builds IoT soil sensors that measure soil moisture, temperature, and electric conductivity, enabling farmers to approach each crop’s unique needs individually. Combined with geospatial data, this technology helps create precise soil maps for each field. Mothive offers similar services, helping farmers reduce waste, improve yields, and increase farm sustainability.
6. Agricultural drones
Perhaps one of the most promising agritech advancements is the use of agricultural drones in smart farming. Also known as UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles), drones are better equipped than airplanes and satellites to collect agricultural data. Apart from surveillance capabilities, drones can also perform a vast number of tasks that previously required human labor: planting crops, fighting pests and infections, agriculture spraying, crop monitoring, etc.
Read more: Why Use Agriculture Drones? Main Benefits and Best Practices
DroneSeed, for example, builds drones for planting trees in deforested areas. The use of such drones is 6 times more effective than human labor. A Sense Fly agriculture drone eBee SQ uses multispectral image analyses to estimate the health of crops and comes at an affordable price.

7. Predictive analytics for smart farming
Precision agriculture and predictive data analytics go hand in hand. While IoT and smart sensor technology are a goldmine for highly relevant real-time data, the use of data analytics helps farmers make sense of it and come up with important predictions: crop harvesting time, the risks of diseases and infestations, yield volume, etc. Data analytics tools help make farming, which is inherently highly dependent on weather conditions, more manageable and predictable.
For example, the Crop Performance platform helps farmers access the volume and quality of yields in advance, as well as their vulnerability to unfavorable weather conditions, such as floods and drought. It also enables farmers to optimize the supply of water and nutrients for each crop and even select yield traits to improve quality.
Applied in agriculture, solutions like SoilScout enable farmers to save up to 50% of irrigation water, reduce the loss of fertilizers caused by overwatering, and deliver actionable insights regardless of season or weather conditions.
8. End-to-end farm management systems
A more complex approach to IoT products in agriculture can be represented by the so-called farm productivity management systems. They usually include a number of agriculture IoT devices and sensors installed on the premises, as well as a powerful dashboard with analytical capabilities and in-built accounting/reporting features.
This offers remote farm monitoring capabilities and allows you to streamline most of the business operations. Similar solutions are represented by FarmLogs and Cropio.
In addition to the listed IoT agriculture use cases, some prominent opportunities include vehicle tracking (or even automation), storage management, logistics, etc.
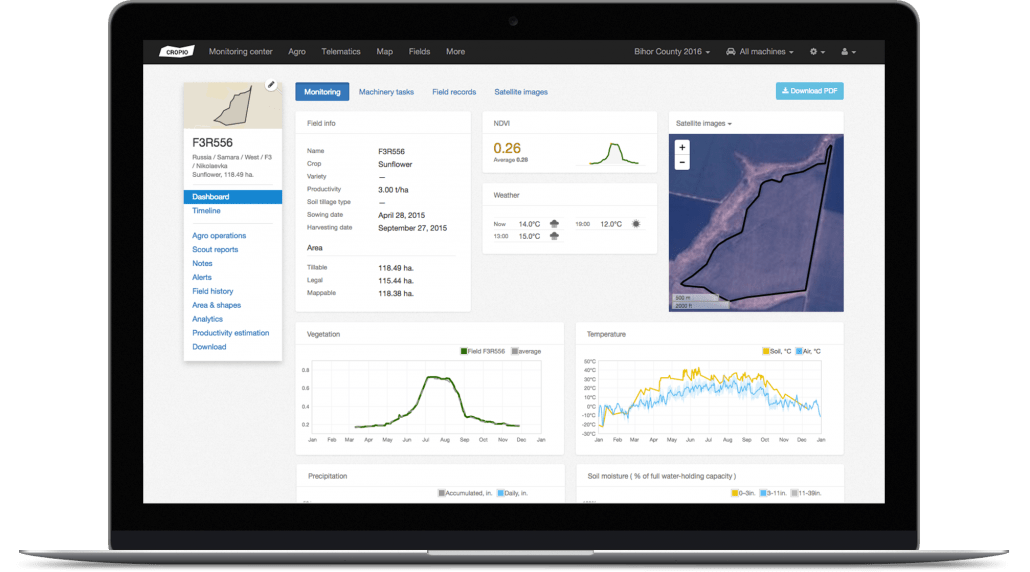
9. Robots and autonomous machines
Robotic innovations also offer a promising future in the field of autonomous machines for agricultural purposes. Some farmers already use automated harvesters, tractors, and other machines and vehicles that can operate without a human controlling them. Such robots can complete repetitive, challenging, and labor-intensive tasks.
For instance, modern agrobots include automated tractors that can work on assigned routes, send notifications, start work at planned hours, etc. Such tractors are driverless and cut farmers’ labor costs. Bear Flag Robotics is one company that works on such technology at the moment.
In addition, smart farming also uses robots for planting seeds, weeding, and watering. The given jobs are very demanding and labor-intensive. Yet, robots, such as those from Eco Robotics, can detect weeds or plant seeds using computer vision and AI technology. These agricultural robots work delicately, drastically reducing harm to the plants and the environment.
Things to consider before developing your smart farming solution
As we can see, the use cases for IoT in agriculture are endless. There are many ways smart devices can help you increase your farm’s performance and revenue. However, agriculture IoT app development is no easy task.
There are certain challenges you need to be aware of if you are considering investing in smart farming.
1. The hardware
To build an IoT solution for agriculture, you need to choose the sensors for your device (or create a custom one). Your choice will depend on the types of information you want to collect and the purpose of your solution in general.
In any case, the quality of your sensors is crucial to the success of your product: it will depend on the accuracy of the collected data and its reliability.
2. The brain
Data analytics should be at the core of every smart agriculture solution. The collected data itself will be of little help if you cannot make sense of it.
Thus, you need to have powerful data analytics capabilities and apply predictive algorithms and machine learning in order to obtain actionable insights based on the collected data.
3. The maintenance
Maintenance of your hardware is a challenge that is of primary importance for IoT products in agriculture, as the sensors are typically used in the field and can be easily damaged.
Thus, you need to make sure your hardware is durable and simple to maintain. Otherwise you will need to replace your sensors more often than you would like.
4. The mobility
Smart farming applications should be tailored for use in the field. A business owner or farm manager should be able to access the information on-site or remotely via a smartphone or desktop computer.
Plus, each connected device should be autonomous and have enough wireless range to communicate with the other devices and send data to the central server.
5. The infrastructure
To ensure that your smart farming application performs well (and to make sure it can handle the data load), you need a solid internal infrastructure.
Furthermore, your internal systems have to be secure. Failing to properly secure your system only increases the likelihood of someone breaking into it, stealing your data, or even taking control of your autonomous tractors.
6. Connectivity
The need to transmit data between many agricultural facilities still poses a challenge for the adoption of smart farming. Needless to say, the connection between these facilities should be reliable enough to withstand bad weather conditions and to ensure non-disruptive operations.
Today, IoT devices still use varying connection protocols, although the efforts to develop unified standards in this area are currently underway. The advent of 5G and technologies like space-based Internet will, hopefully, help find a solution to this problem.
7. Data collection frequency
Because of the high variety of data types in the agricultural industry, ensuring the optimal data collection frequency can be problematic. The data from field-based, aerial, and environmental sensors, apps, machinery, and equipment, as well as processed analytical data, can be a subject of restriction and regulations.
Today, the safe and timely delivery and sharing of this data is one of the current smart farming challenges.
8. Data security in the agriculture industry
Precision agriculture and IoT technology imply working with large sets of data, which increases the number of potential security loopholes that perpetrators can use for data theft and hacking attacks. Unfortunately, data security in agriculture is still, to a large extent, an unfamiliar concept.
Many farms, for example, use drones that transmit data to farm machinery. This machinery connects to the Internet but has little to zero security protection, such as user passwords or remote access authentications.
Some of the basic IoT security recommendations include monitoring data traffic, using encryption methods to protect sensitive data, leveraging AI-based security tools to detect traces of suspicious activity in real-time, and storing data in the blockchain to ensure its integrity.
To fully benefit from IoT, farmers will have to get familiar with the data security concept, set up internal security policies, and adhere to them.
Our work case of IoT solutions for agriculture
Our team at Eastern Peak has also contributed to the progress of IoT applications in agriculture. The IoT-powered irrigation application, GreenIQ, helps gardeners reduce water usage by 50%, monitor humidity levels, and predict the best timing for irrigation. GreenIQ uses smart sensors to analyze meteorological conditions and soil types, creating the perfect irrigation strategy and adapting to new environments.
The GreenIQ application also integrates with the most well-known home automation platforms. This app is another valuable contribution to eco-friendly gardening and one of many examples of how smart farming products can change the future of agriculture.

Grow your agriculture business with smart IoT solutions from Eastern Peak
According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the global population is expected to surpass 9 billion people by 2050. To produce enough food for the given population, agricultural production volumes have to increase by 50%.
As the resources for agricultural operations are limited (most of the lands suitable for farming are already in use), the only way to increase volume is to improve production efficiency. There is no doubt as to the extent to which smart farming can help tackle this challenge; in fact, it seems that it is not possible without it. Here at Eastern Peak, we develop custom IoT solutions for agriculture, tailored to your particular needs.
How to get started?
From cattle tracking to advanced field mapping, IoT applications in smart agriculture vary from farm to farm depending on your market segment, climate, and region. In many instances, out-of-the-box tools won’t be relevant, and you may need a tailored smart farming IoT solution. At Eastern Peak, we approach each customer individually to meet their unique needs.
The product discovery phase is the best first step you can take to lay a solid foundation for the development of your app. It includes a functional specification, UX/UI design, and a visual prototype that will give you a clear vision of the end product. On average, this phase takes 4-6 weeks.
The product discovery phase can help you:
- define a full scope of work and develop a roadmap for the project
- set a realistic budget for your MVP and plan your resources
- test the waters with your audience using a visual prototype
- craft a convincing investment pitch
- get to know your team
We at Eastern Peak have already helped many startups and Fortune 500 companies digitize and streamline their operations with the help of technologies. We provide end-to-end services building IoT solutions across a number of business domains, from hardware design to software development, testing, and integration.
To receive professional consultation from our experts, get in touch with us using our contact form.
Read also:
- Smart Farming: How Automation Is Transforming Agriculture
- 3 Edge Computing Use Cases for Smart Farming
- Smart Agriculture Monitoring Solutions to Optimize Farming Productivity
- 6 Cool Examples of Internet of Things Applications and How to Develop One
- Shaping the Future of Agriculture Through AI-Powered Solutions



